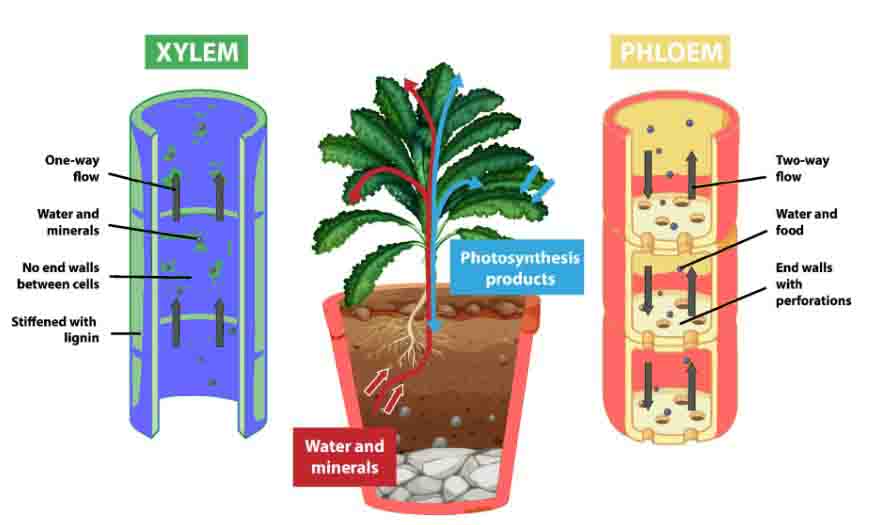
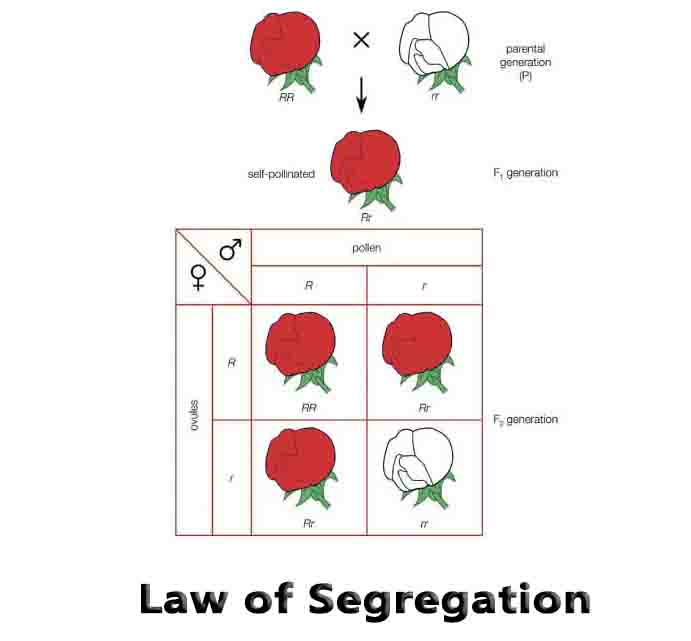
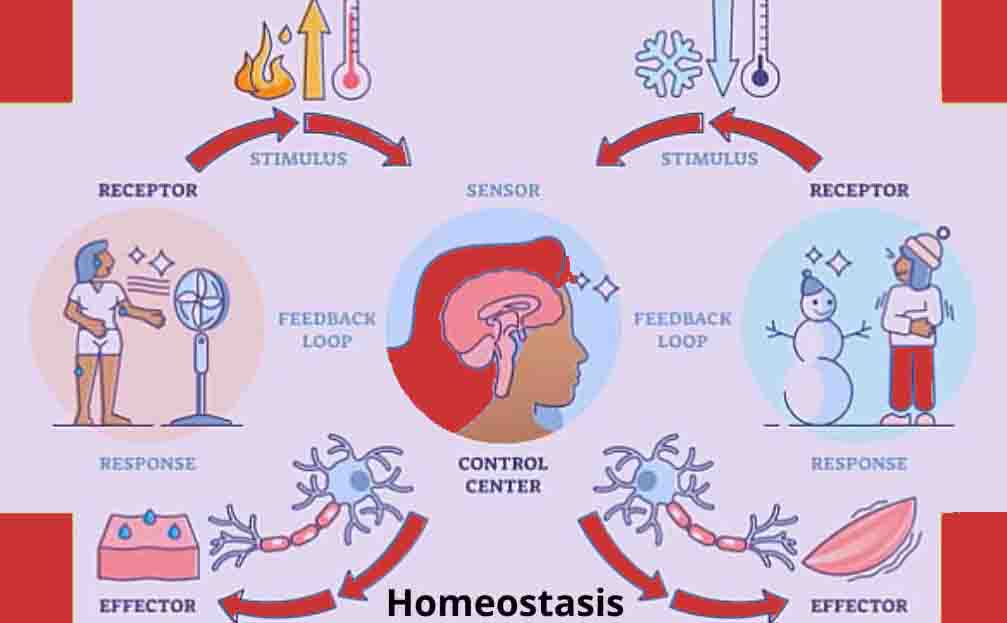
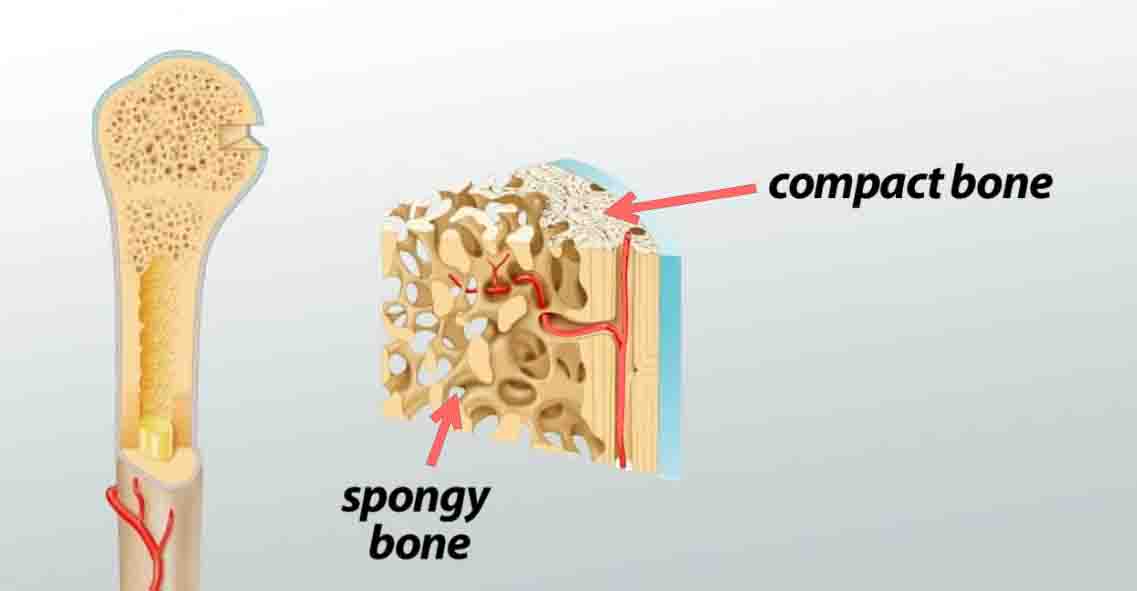
Polygenic Traits
Polygenic Traits Definition Rather than being controlled by just one gene, polygenic traits are controlled by multiple genes. They may be controlled by genes located near each other or even on different chromosomes. Mendel’s inheritance pattern does not apply to polygenic traits because multiple genes are involved. As opposed to being measured discretely, they are … Read more